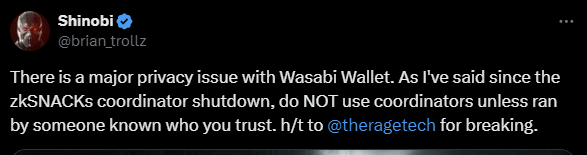
WabiSabi Vulnerability Allows Malicious Coordinators to Deanonymize Coinjoin Users
A vulnerability in the WabiSabi protocol allows malicious coordinators to deanonymize users' coins and link inputs to outputs, compromising the privacy of coinjoin participants. Users are urged to update their instances immediately.

- The vulnerability affects Wasabi Wallet v2.2.1.0 or earlier, Ginger Wallet v2.0.13 or earlier, and BTCPay coinjoin plugin v1.0.101.0 or earlier.
"Given that this attack can be carried out without raising suspicion and the lack of client-side checks on previously issued events, the vulnerability is highly exploitable by any party running the coordination services," reported the team behind Ginger Wallet.
NOTE: Ginger Wallet is a fork of Wasabi Wallet that screens coinjoin round inputs with a chain surveillance partner company.
- The affected versions of the WabiSabi protocol have a vulnerability due to inadequate client-side validation of credential issuers. It allows malicious coordinators to use multiple issuers to differentiate inputs from outputs, trace input ownership, and break the anonymity set of Bitcoin's coinjoin process, compromising user privacy.

- Any malicious coordinator with full control over a coinjoin round can exploit the vulnerability without needing special privileges or external tools, making it easy to compromise user privacy.
"We believe that this vulnerability is not actively being exploited. Based on tests conducted on three of the most popular coordinators, the round state responses were consistent in all cases," added the GingerPrivacy team.
Disclosure
The Rage Article / Archive
Bitcoin Magazine Article / Archive




